Creating a new instrument capable of detecting trace amounts of uranium and other materials will be the focus of a new research partnership spearheaded by scientists at Colorado State University.
The partnership, led at CSU by University Distinguished Professor Carmen Menoni of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, is supported by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Domestic Nuclear Detection Office through its Nuclear Forensics Research Award(NFRA) program.
OSU says that together with researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Menoni will oversee the design and implementation of a highly sensitive mass spectrometer capable of detecting just a few uranium atoms at a time. The instrument will also allow nanoscale imaging of the isotopic content of solid samples, in three dimensions. Such a tool could set the stage for new capabilities in nuclear forensics, to support U.S. government counter-nuclear-terrorism efforts.
The nuclear forensics award will bring Pacific Northwest National Laboratory scientist Lydia Rush to CSU as a Ph.D. student in Menoni’s lab. The collaboration will involve training Rush and other students in cutting-edge, laser-based mass spectral imaging and forensics.
Existing tech, unprecedented sensitivity
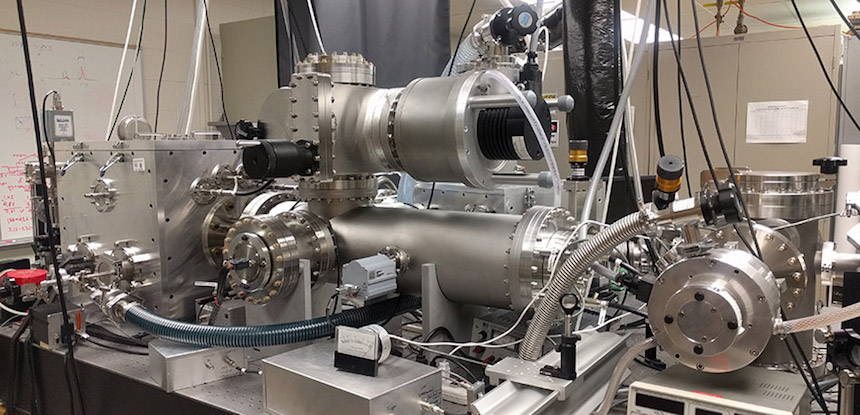
“The new instrument we are going to build is going to be far more sensitive than our previous-generation, extreme ultraviolet time-of-flight mass spectrometry instrument,” Menoni said. “It will employ a magnetic sector to identify uranium, thorium and their isotopes at a concentration of a few parts per million.”
The imaging technology provides unprecedented sensitivity and spatial resolution because it uses an extreme ultraviolet laser for ablation and ionization. This compact laser is an innovation from the lab of University Distinguished Professor Jorge Rocca.
The laser ablation process creates a plume of ionized atoms and molecules, which the detector reads inside a vacuum chamber. A set of special plates allows the scientists to extract and detect ions from the sample, identifying uranium (or other elements) by determining its unique ion signature, like a fingerprint.
Identifying minute amounts of various compounds has its uses in national security, but could also be applied to any process requiring identification of very small amounts of molecules.


