Many countries are failing to comply with the non-binding commitments of the Paris Agreement, making it increasingly clear that we have to reconsider how to ensure collective action to limit global warming to less than 2°C above preindustrial levels. A new IIASA-led study supports a different approach to designing an international climate agreement that would incentivize countries to cooperate.
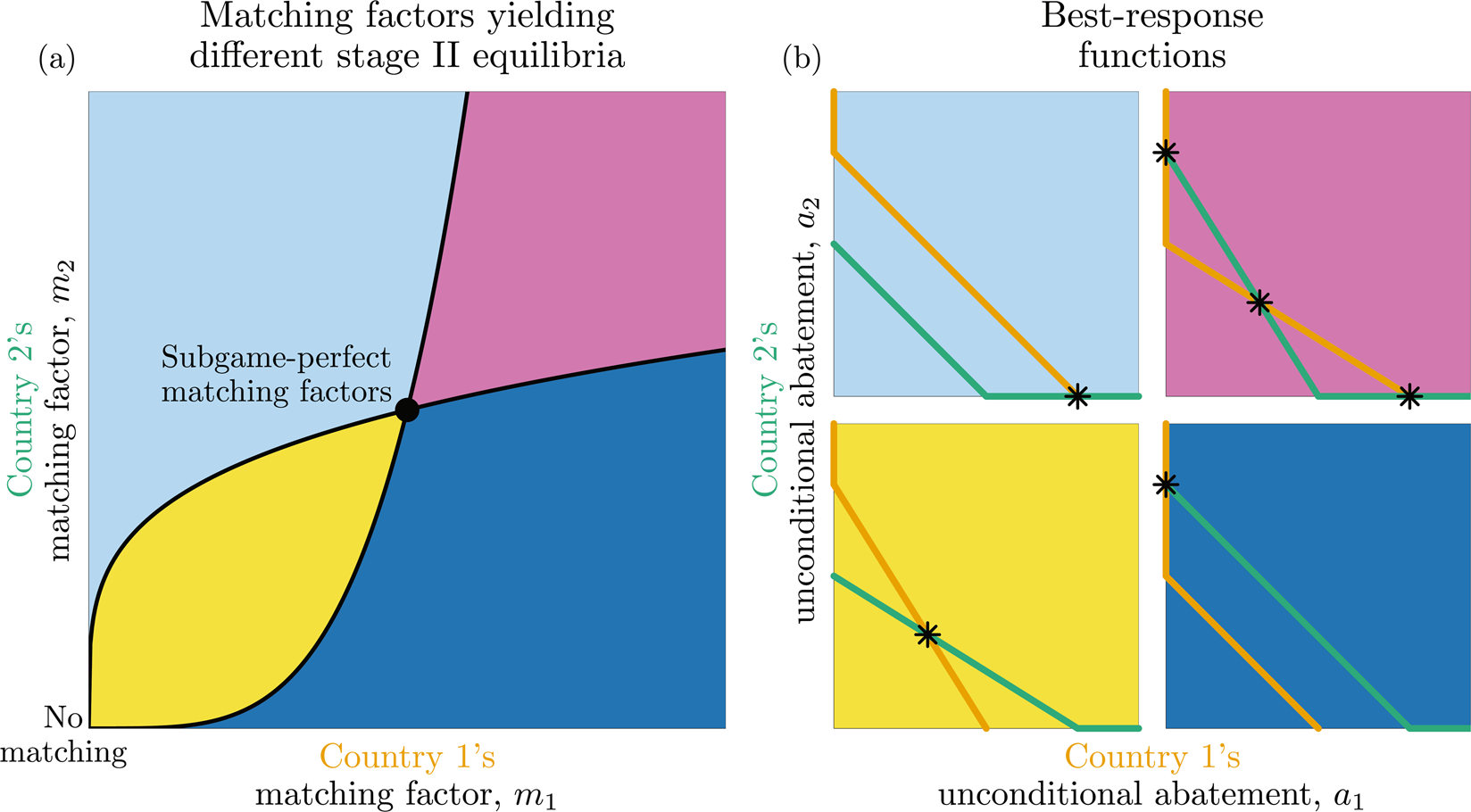
Although there is general consensus that global greenhouse gas emissions are too high, most governments would prefer other countries to reduce their emissions rather than reducing their own. The Paris Agreement is intended to solve this collective action problem, but according to a 2017 United Nations Environment Programme report, this landmark accord is likely insufficient. The authors of the study published in Scientific Reports explored one proposed solution to this problem, namely matching-commitment agreements. In such an agreement, each country can commit to reducing its emissions by an amount that depends on the emissions reductions of other countries. Using these commitments to conditional emissions reductions allows countries to incentivize other countries to reduce their emissions.
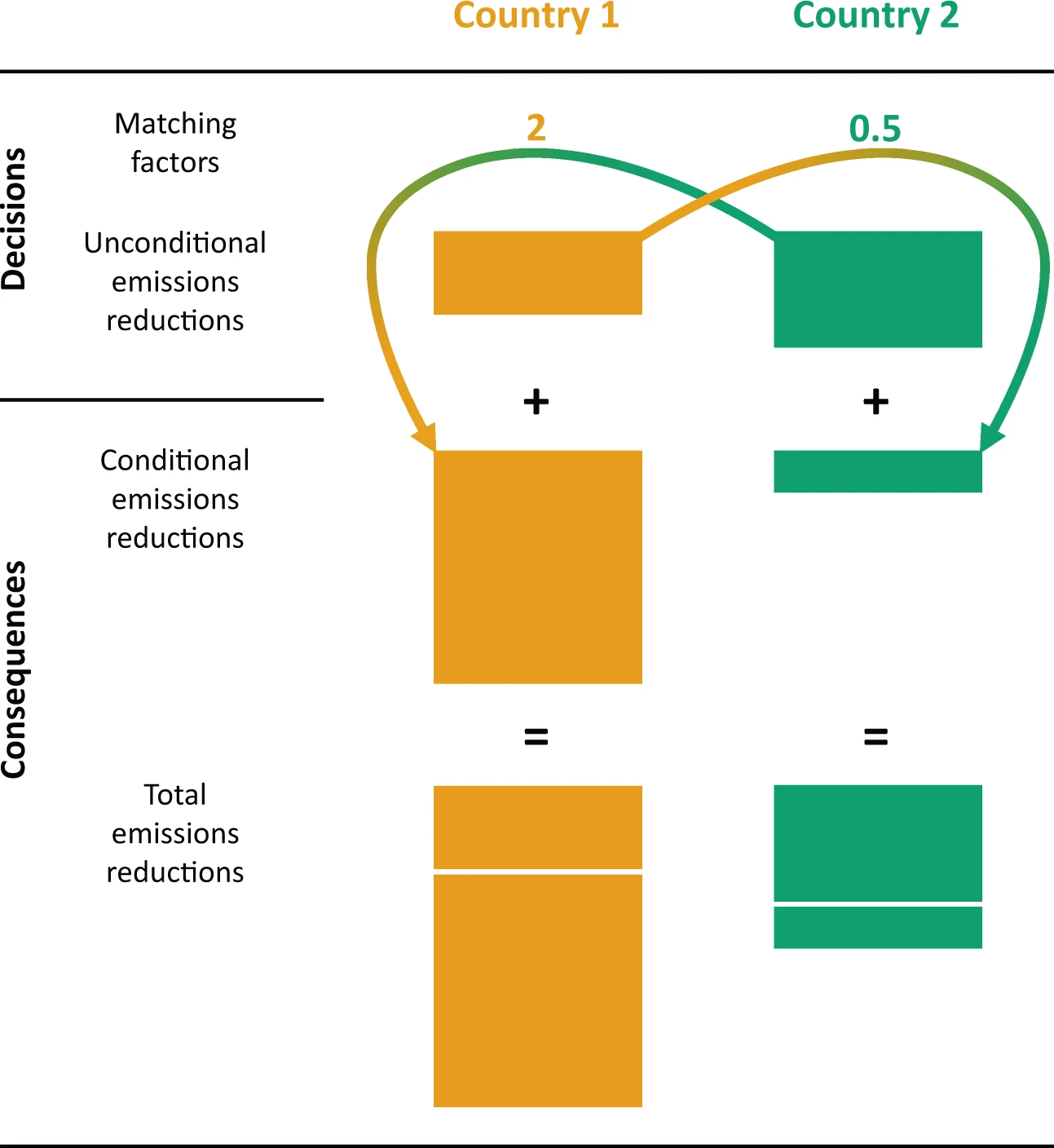
“Much of the current discussion around international climate agreements centers on how to induce countries to accede to a global carbon price, and prevent countries who do not impose such a tax from gaining an economic advantage over those who do. One prominent approach to doing so is the “climate club” approach, which incentivizes countries to cooperate by imposing trade sanctions on those who do not. While this approach is compelling and may avoid some of the shortcomings of the Paris Agreement, its implementation would be difficult, as international-trade law would need to be amended to allow for penalties on non-participants,” explains study lead author Chai Molina, a researcher at IIASA, Princeton University, and the University of Pennsylvania. “We wanted to understand if it’s possible to incentivize countries to cooperate by using a matching-commitment agreement rather than trade sanctions or asking them to make binding commitments to unilateral actions.”
The study results indicate that such an agreement incentivizes countries to make matching commitments that in turn incentivize emissions reductions and reduce emissions from those expected without an agreement. In the one-shot “climate game” analyzed in the study, matching-commitment agreements successfully diverted two heterogeneous countries from a rational, stable outcome from which no country has an incentive to deviate, to a unique new, efficient equilibrium at which their emissions are lower than they would be in the absence of an agreement. At this new equilibrium, both countries are better off in terms of their economic payoffs than they would have been without the matching-commitment agreements.
The authors say that one of the aspects that makes their study different from other studies on matching-commitment agreements, is that most of them treat countries as if they were identical, assuming that they would suffer the same damages from climate change, and that they have the same selfish economic incentives to keep greenhouse gas emissions high. This research was inspired by a previous study that analyzed matching-commitment agreements between countries whose incentives may be different from one another. That study, however, considered a business-as-usual scenario in which some countries act irrationally, in the sense that they have an incentive to lower their emissions unilaterally, but do not do so. In this setting, it is unclear whether the matching-commitment agreement results in emissions reductions beyond those that would have been achieved without any agreement, if countries simply heeded their selfish incentives.
In their study, the authors analyzed a more realistic scenario in which countries consistently respond rationally to their incentives, both in the business-as-usual scenario and under a matching-commitment agreement. This new choice of business-as-usual is important, not just because it changes the payoffs countries obtain for different emissions reductions, but also because it allowed the authors to show that the matching-commitment agreement still results in reduced emissions, even if countries heed their economic incentives in the absence of an agreement.
The researchers emphasize that their work is a “proof of concept”, and that further work on the subject will help to determine whether these agreements would work in practice. Nonetheless, the study results suggest that matching-commitment agreements are a promising approach to constructing an international environmental agreement. Moreover, a similar approach could in principle be used to tackle other public goods problems in situations in which enforcement is problematic.


